Majority of Households in the Island Areas Own a Computer and Have Broadband Internet
Demographic profiles for the 2020 Island Areas Censuses (IACs) released today show that at least 90% of households report owning a computer, and 69% or more had access to a broadband internet subscription.
The IACs highlight computer ownership and internet use in the Island Areas every 10 years for American Samoa, the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands (CNMI), Guam, and the U.S. Virgin Islands.
For context, 95% of U.S. households owned a computer and 90% had a broadband internet subscription, according to national estimates from the 2021 American Community Survey (ACS), which collects demographic, economic, and housing data for 50 states, the District of Columbia, and Puerto Rico annually.
The addition of smartphones, tablets and other devices was new to the 2020 IACs; in the 2010 census, households could only report desktop computer or laptop ownership.
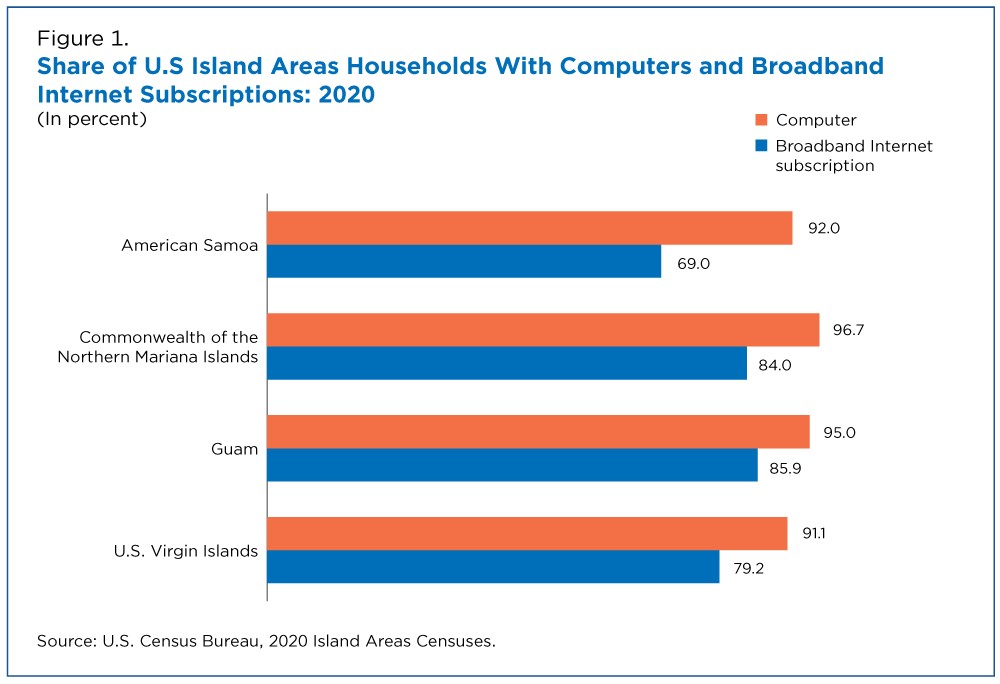
Figure 1 displays the results of the 2020 IACs for computer ownership and internet use for each of the Island Areas:
- The Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands had the highest rate of computer ownership, with approximately 97% of households reporting ownership of at least one type of computer and 84% reporting having a broadband internet subscription.
- American Samoa had the lowest rate of broadband subscription out of all the Island Areas, with 69% of households there indicating they subscribed to one or more broadband services. Ninety-two percent of households in American Samoa owned a computer.
- In Guam, 95% of households owned a computer and 85% had a broadband internet subscription.
- In the U.S. Virgin Islands, 91% of households owned a computer and 79% had a broadband subscription.
Given the cultural, geographic and socioeconomic differences across the Island Areas, we suggest using caution when comparing estimates across Island Areas. Additional information on the data collection for these islands is available on the IACs technical documentation page.
Changes to Questions on Computer and Internet Use
2020 IACs computer and internet use questions were updated to align with changes made to the 2016 American Community Survey (Figure 2).
In 2020, households could report owning one or more types of computing devices from four possible categories: desktop or laptop computer, smartphone, tablet or another portable device or some other type of computing device.
The addition of smartphones, tablets and other devices was new to the 2020 IACs; in the 2010 census, households could only report desktop computer or laptop ownership.
Similarly, questions about internet subscription were expanded to identify both subscription status and the type of internet connection from five categories: cellular data plan, broadband, satellite, dial-up or some other service.
Respondents could indicate each connection type that applied to their household. In 2010, respondents were only asked to identify whether their household had internet access.
Comparing Island Areas Censuses Data: 2010 and 2020
Direct comparisons between the IACs 2010 and 2020 data should be made with caution.
Differences in question wording, question scope and data collection methods affected by the COVID-19 pandemic should all be considered when drawing conclusions from the data. As mentioned above, one key difference is that the 2010 questions for computer ownership and internet subscription had fewer response options while the 2020 questions were expanded to account for changes in available technologies such as smartphones and tablets.
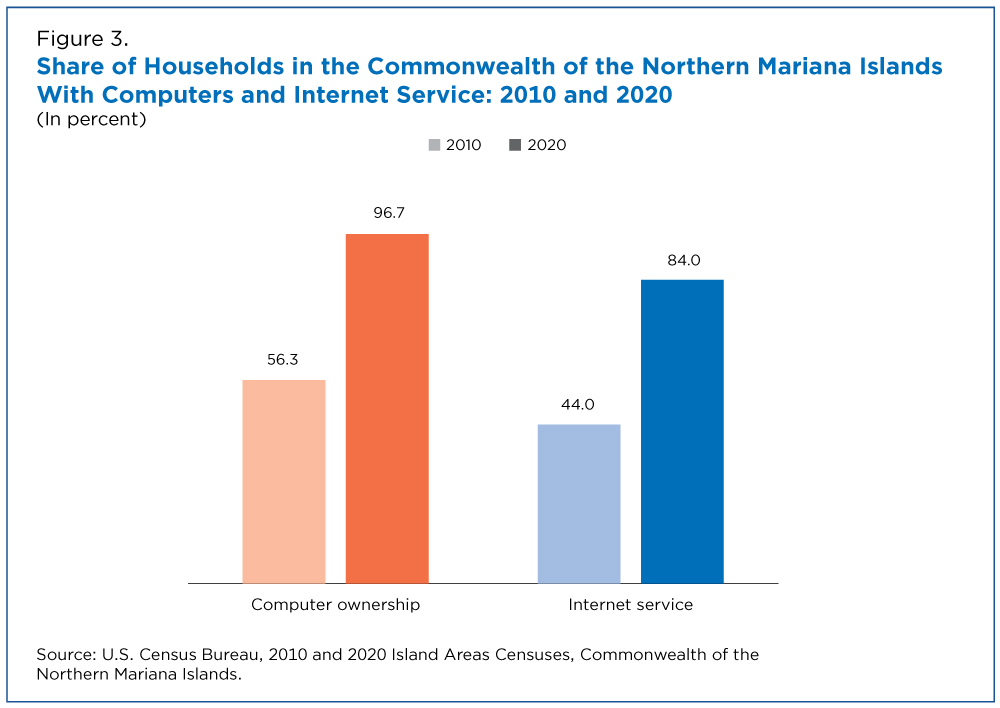
With these considerations in mind and using the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands as an example, Figure 3 illustrates the types of changes seen in the Island Areas between 2010 and 2020.
Computer ownership and internet subscriptions in the CNMI both increased from 2010 to 2020. Computer ownership went from 56% in 2010 to 97% in 2020, while household access to an internet service increased from 44% to 84%.
Potential Sources of Broadband Growth
Growth in computer ownership and internet subscription, such as that seen in CNMI, is not surprising. Technological advances and the expansion of broadband infrastructure has made computing technology both more affordable and more common.
Over the past decade, motivating factors for using the internet have increased, such as for entertainment as well as necessary services like health care and education.
Additionally, the past decade has seen several investments in broadband infrastructure in Island Areas, each of which may have affected growth in subscription rates over this period.
The American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009 led to several grants awarded across the Island Areas to expand broadband internet infrastructure, enhance and expand public computer centers, and encourage the sustainable adoption of broadband service. These grants were awarded beginning in 2010.
CNMI, for example, received a portion of over $24 million in grants disbursed by the National Telecommunications and Information Administration (NTIA) to fund programs related to developing infrastructure, adoption of available services and improving data on broadband.
Further, in June 2017, the Atisa undersea fiber-optic cable became operational, connecting CNMI to Guam with internet service. This cable complemented the last completed cable to CNMI, the Mariana-Guam cable, which was completed in 1997.
Related Statistics
-
Stats for StoriesNational Caribbean-American Heritage Month: June 2023According to the 2023 International Database, the three most populous Caribbean countries are Haiti (11.5M), Cuba (11.0M) and the Dominican Republic (10.8M).
-
Facts for Features & Special EditionsAsian American and Pacific Islander Heritage Month: May 2022A host of statistical information on the Asian and Native Hawaiian and Other Pacific Islander population groups.
-
Video TutorialsOur team has created a series of "how-to" videos for those looking for ways to enhance their knowledge of data.census.gov, Census API, and Microdata Access.
Subscribe
Our email newsletter is sent out on the day we publish a story. Get an alert directly in your inbox to read, share and blog about our newest stories.
Contact our Public Information Office for media inquiries or interviews.
-
America Counts StoryMapping Digital Equity in Every StateMay 13, 2022The new Digital Equity Act Population Viewer will help meet the funding goals of the Digital Equity Act of 2021.
-
America Counts StoryFirst 2020 Census U.S. Island Areas Data Released TodayOctober 28, 2021The first 2020 U.S. Island Areas Censuses shows that the combined population of the four U.S. Island Areas was just under 339,000 in 2020.
-
America Counts StoryE-Commerce Sales Surged During the PandemicApril 27, 2022Annual growth in e-commerce retail sales accelerated during the pandemic as more consumers shopped online.
-
IncomeHow Income Varies by Race and GeographyJanuary 29, 2026Median income of non-Hispanic White households declined in five states over the past 15 years: Alaska, Connecticut, Louisiana, Nevada, and New Mexico.
-
HousingShare of Owner-Occupied, Mortgage-Free Homes Up in 2024January 29, 2026The share of U.S. homeowners without a mortgage was higher in 2024 than a decade earlier nationwide and in every state, though not all counties saw increases.
-
HousingRental Costs Up, Mortgages Stayed FlatJanuary 29, 2026Newly Released American Community Survey compares 2020-2024 and 2015-2019 housing costs by county.
-
PopulationU.S. Population Growth Slowest Since COVID-19 PandemicJanuary 27, 2026The decline in international migration was felt across the states, though its impact varied.