What Is A Used Vehicle?
What Is A Used Vehicle?

It is always a great moment when you buy a car. It does not matter if it’s used or the dream car that you always wanted since you were a kid. Even if it has over 100,000 miles, the first time you open its doors, you still get that “new car smell” and treat it as a brand new car. That brings me to today’s topic: how to determine what is a used car in the Automated Export System (AES).
How does AES define a Used Vehicle?
A used vehicle, according to Customs and Border Protection CFR 192.2 , is defined as “any self-propelled vehicle the equitable or legal title to which has been transferred by a manufacturer, distributor, or dealer to an ultimate purchaser .”
What does that mean? It means that unless you’re buying a car directly from the manufacturer, it’s used. That’s right, a car coming out of the dealership is used. Another example of a used vehicle (for AES purposes) would be if you bought a vehicle online and have not even seen it physically yet.
Now that you have determined that your car is considered a used vehicle for the AES, what would be required to complete the Electronic Export Information (EEI)?
In AESDirect, you need to select “Yes” under the question “Is this commodity a Used Vehicle?”
Then complete the fields:
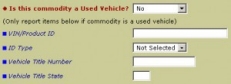
- VIN/Product ID: Provide the Vehicle Identification Number. If not available, you can submit a Product Identification Number for the vehicle.
- ID Type: Identify the type of identification number reported
- Vehicle Title Number: Report the title number for the car
- Vehicle Title State: Indicate the state where the title was issued
If you do not provide this information, the system will not allow you to submit your EEI.
Only certain Schedule B numbers will allow you to report used vehicles and to complete those additional fields. See Rosanna's post on this.



