Census.gov > Library > Infographics & Visualizations > 2012 > By the Grid: Population Shift to the West and South
Library
By the Grid: Population Shift to the West and South
October 18, 2012
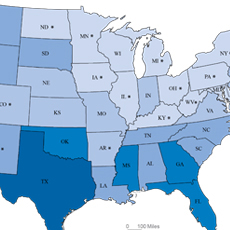
The 100th meridian generally defines the boundary between the humid eastern and arid western parts of the country. Historically, living west of the 100th meridian has meant a reliance on irrigation for successful agriculture and substantial settlements were limited in size. The 38th parallel divides the country based on average July temperature, with most of the country below the parallel experiencing average July temperatures of over 80 degrees. The completion of large-scale dam projects in the early 20th century generated water and electricity that made it possible for large cities to develop in the West. The widespread use of air conditioning after the 1970s helped make living in hotter parts of the country more tolerable.
SOURCE: Decennial censuses 1790 to 2010
NOTE: Data were derived from population-weighted county centroids and decennial census data.
Recent Data Visualizations
 Population Without Health Insurance
Population Without Health Insurance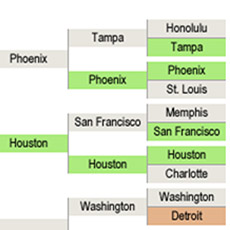 Population Bracketology
Population Bracketology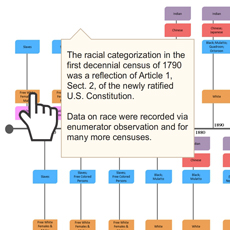 Measuring Race and Ethnicity Across the Decades: 1790-2010
Measuring Race and Ethnicity Across the Decades: 1790-2010  Where do college graduates work?
Where do college graduates work? Story Maps Illustrate Population Change
Story Maps Illustrate Population Change HIV/AIDS Impact in Africa
HIV/AIDS Impact in Africa Distribution of Hispanic or Latino Population by Specific Origin: 2010
Distribution of Hispanic or Latino Population by Specific Origin: 2010 A Century of Population Change in the Age and Sex Composition of the Nation
A Century of Population Change in the Age and Sex Composition of the Nation  Shifting Occupational Shares
Shifting Occupational Shares Metro Area Density
Metro Area Density Work-Life Earnings
Work-Life Earnings Census Flows Mapper
Census Flows Mapper Migration Between Calif. & Other States
Migration Between Calif. & Other States U.S. Territory and Statehood Status
U.S. Territory and Statehood Status Spoken Languages Other than English
Spoken Languages Other than English Center of Population, 1790-2010
Center of Population, 1790-2010 Population Change by Decade
Population Change by Decade Without A High School Education
Without A High School Education A Decade of State Population Change
A Decade of State Population Change State-to-State Migration for States of 8 Million or More
State-to-State Migration for States of 8 Million or More Population Under 5 Years Old by Congressional District
Population Under 5 Years Old by Congressional District Components of Metro Area Change
Components of Metro Area Change Blooming States
Blooming States Coastline County Population
Coastline County Population Coastline County Population
Coastline County Population I-90 Population Density Profile, 2010
I-90 Population Density Profile, 2010 Second Cities: Keeping Pace with a Booming New York
Second Cities: Keeping Pace with a Booming New York By the Grid: Population Shift to the West and South
By the Grid: Population Shift to the West and South I-10 Population Density Profile, 2010
I-10 Population Density Profile, 2010 Booming Cities Decade-to-Decade, 1830-2010
Booming Cities Decade-to-Decade, 1830-2010 I-5 Population Density Profile, 2010
I-5 Population Density Profile, 2010 Islands of High Income
Islands of High Income The Great Migration, 1910 to 1970
The Great Migration, 1910 to 1970 Following the Frontier Line, 1790 to 1890
Following the Frontier Line, 1790 to 1890 Changing Ranks of States by Congressional Representation
Changing Ranks of States by Congressional Representation Cartograms of State Populations in 1890, 1950, and 2010
Cartograms of State Populations in 1890, 1950, and 2010 Before and After 1940: Change in Population Density
Before and After 1940: Change in Population Density From Physical to Political Geography
From Physical to Political Geography Differential City Growth Patterns
Differential City Growth Patterns I-95 Population Density Profile
I-95 Population Density Profile Increasing Urbanization
Increasing Urbanization Gaining and Losing Shares
Gaining and Losing Shares Top 20 Cities
Top 20 Cities
 Top 20 Cities
Top 20 CitiesComments or suggestions?